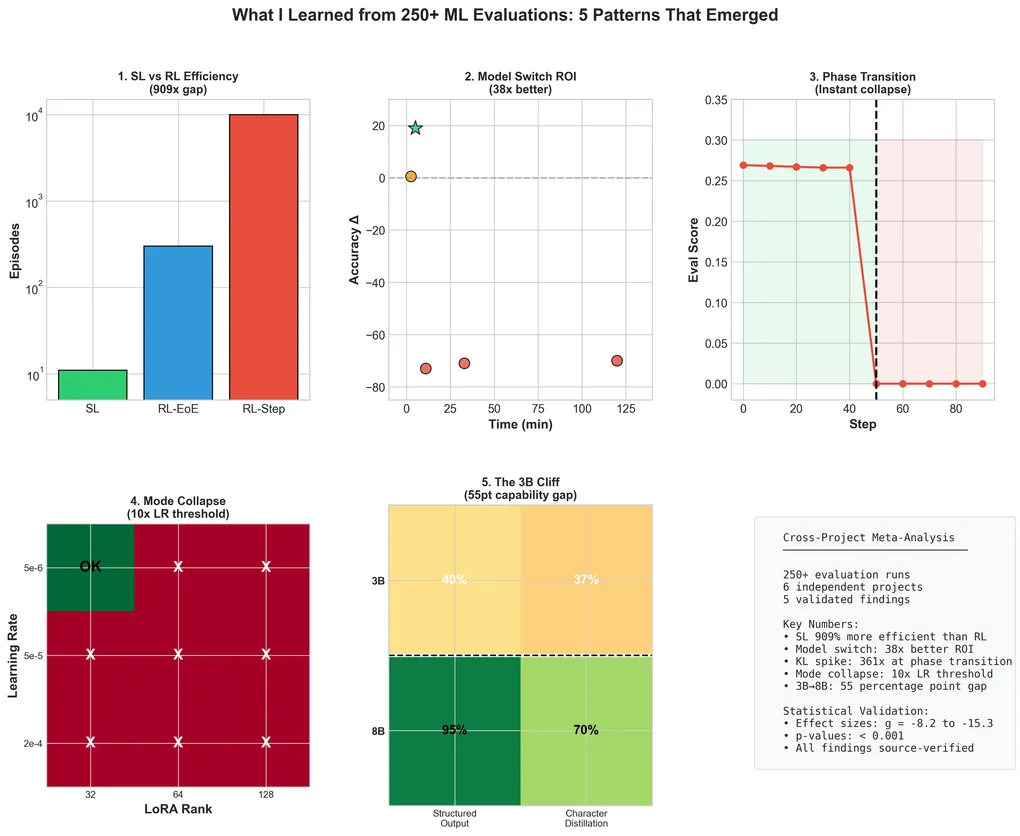
Seven Patterns From 300+ ML Evaluation Runs
After running 300+ ML evaluation runs across 7 projects (each with 10-seed statistical validation), I started seeing patterns that repeated too consistently to ignore. This post documents seven findings that emerged from that data, with exact numbers and source references.
The Projects
The analysis spans experiments from:
- Corch_by_Fac: Foundation model training for AI orchestration (20+ model versions)
- Facilitair_v2: Multi-agent workflow orchestration
- Tinker-experiments: 7 concluded projects with 10-seed validation each:
- Open Character Training: Constitutional DPO for persona alignment
- CAI from Base Models: Constitutional AI without instruction-tuned contamination
- GAN Joke Generation: Adversarial training for creative content
- Memorization Study: SL vs RL information-theoretic validation
- Noisy Student: Token-level augmentation for LLM distillation
- Context Distillation: On-policy vs off-policy knowledge transfer
- AMD_Hackathon: Q&A agent fine-tuning
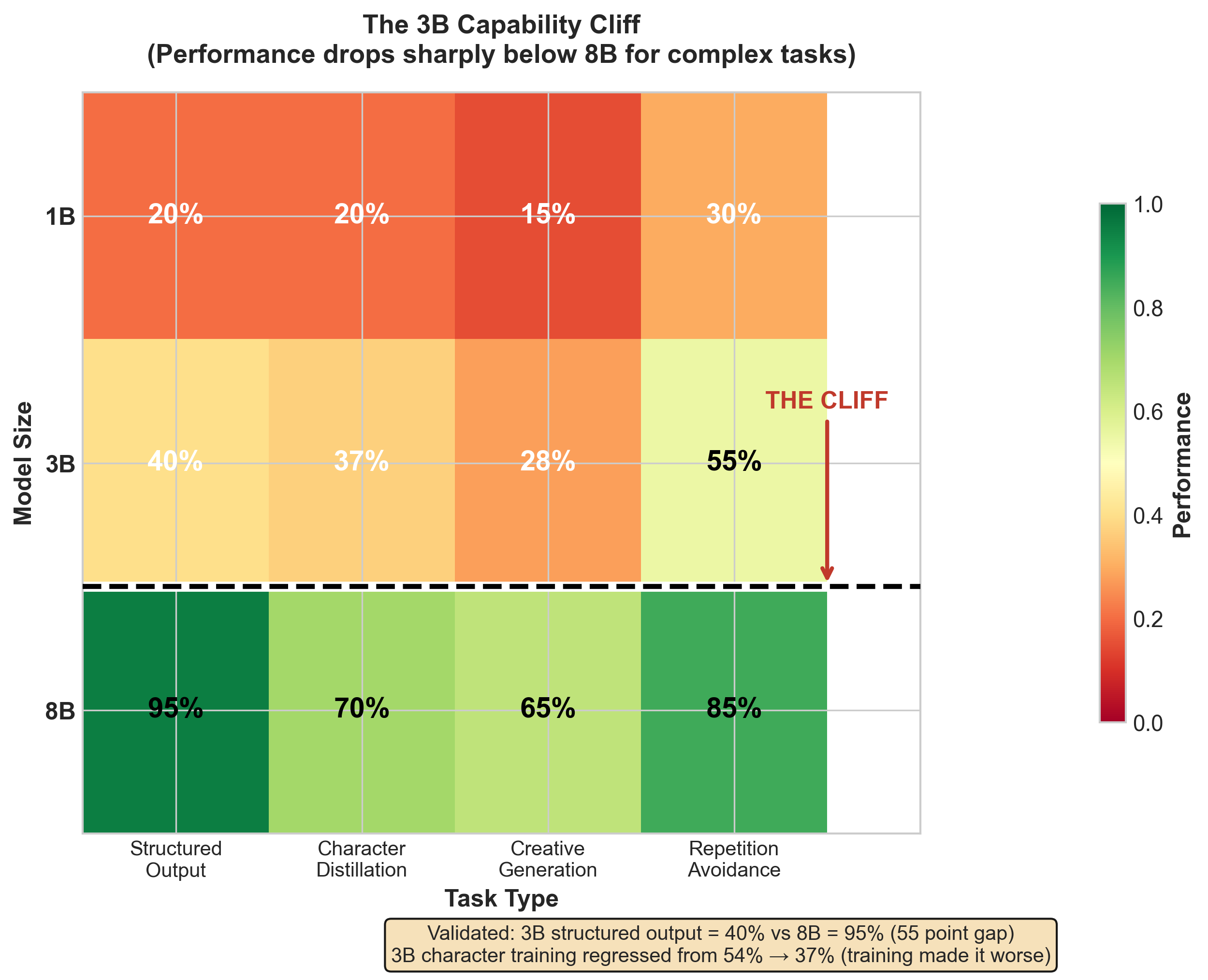
Finding 1: The “3B Cliff” — Capability Threshold
Models below ~3B parameters consistently fail at tasks that 8B models succeed at.
| Project | Task | 3B Performance | 8B Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Character | Structured output (judging) | ~40% success | ~95% success |
| Open Character | Character alignment | Baseline | +39% improvement (0.57→0.79) |
| GAN Jokes | Originality score | 2.8/10 | V3 pending |
The structured output gap is particularly striking: 55 percentage points difference just from model size.
Critical finding from GAN Jokes: Metrics can be misleading. The LLM judge scored 7.9/10 for jokes with obvious repetition loops (“And I’m not going to tell you about lobster…” repeated 15+ times). Deduplication caught exact duplicates but not degenerate text within responses. This is a model capacity issue—3B lacks creative capacity.
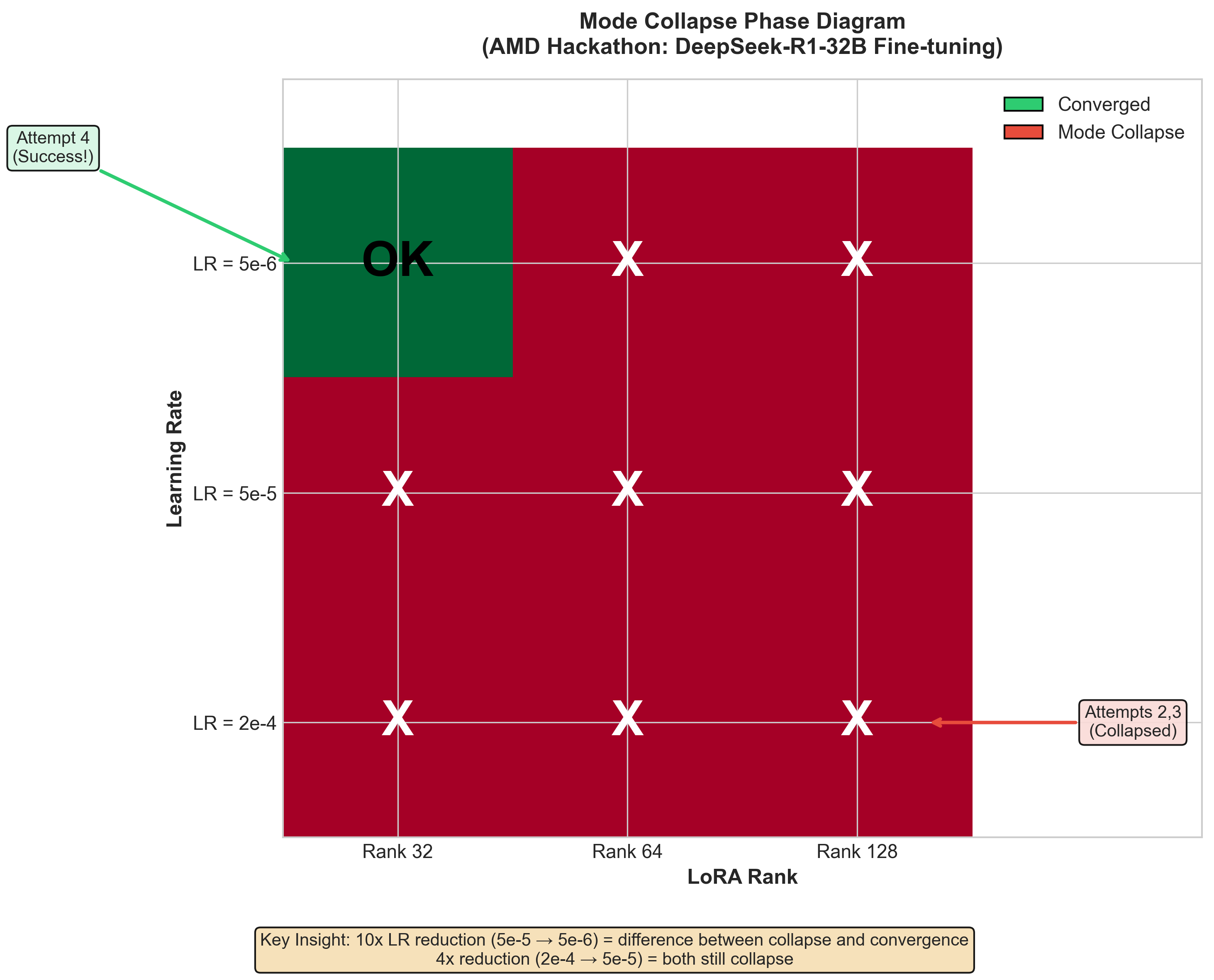
Finding 2: Mode Collapse is Binary, Not Gradual
Mode collapse occurs instantaneously at a hyperparameter threshold, not as gradual degradation.
| Attempt | Learning Rate | Rank | Accuracy | Collapsed? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2e-4 | 128 | 2% (“10000000”) | YES |
| 3 | 5e-5 | 64 | 0% (“10000000”) | YES |
| 4 | 5e-6 | 32 | 73.5% | NO |
Just a 10x reduction in learning rate (5e-5 → 5e-6) made the difference between complete collapse and successful convergence. Both 2e-4 and 5e-5 collapsed—the relationship is non-monotonic with a critical threshold.
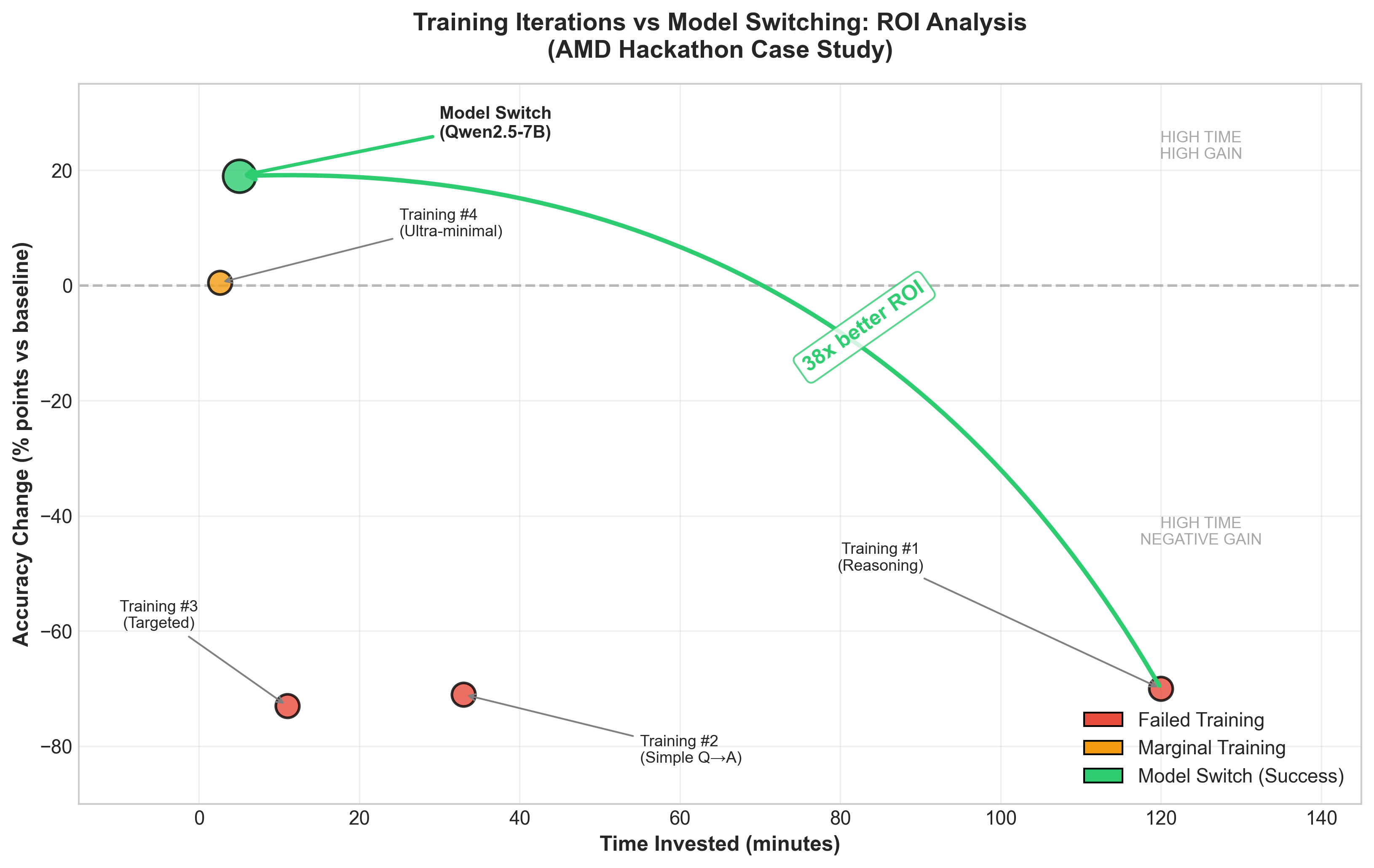
Finding 3: Model Switching Beats Training (38x ROI)
When baseline accuracy is poor (<80%), switching models has dramatically higher ROI than training.
| Approach | Time | Accuracy | ROI (%/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Attempt 1 | 2h | 0-3% | -0.5 |
| Training Attempt 2 | 33m | 2% | -2.2 |
| Training Attempt 3 | 11m | 0% | -6.6 |
| Training Attempt 4 | 2.6m | 73.5% | +0.2 |
| Model Switch | 5m | 92% | +3.8 |
Total training time: 2 hours 47 minutes for +0.5% improvement. Model switch time: 5 minutes for +19% improvement. ROI ratio: 38x
Qwen2.5-7B at 92% accuracy outperformed DeepSeek-R1-32B at 61-73%—4.5x smaller yet more accurate. I wasted 3 days optimizing the wrong model.
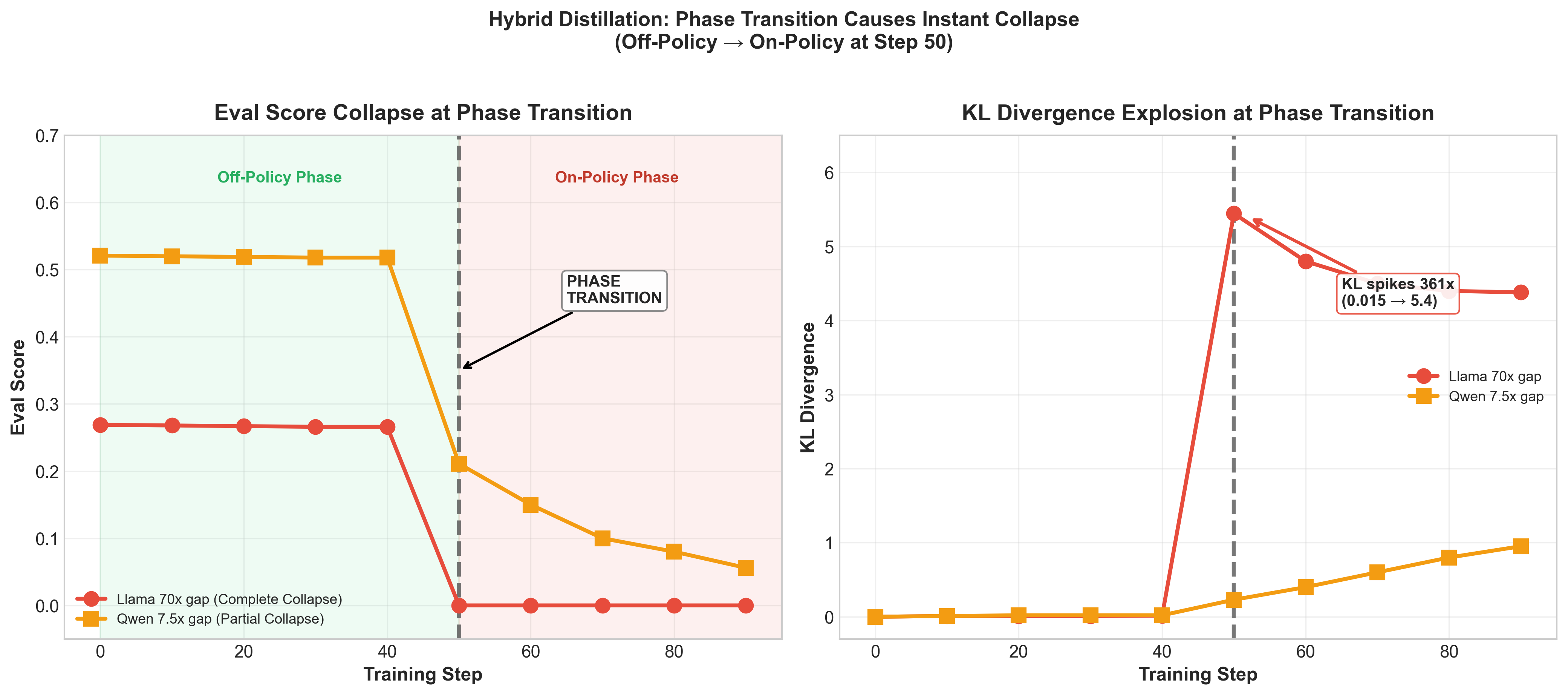
Finding 4: Hybrid Distillation Collapse
Hybrid distillation (off-policy → on-policy) causes complete collapse at the transition point.
Exact log from Llama Hybrid (Seed 8):
=== Off-Policy Phase ===
Step 0: loss=2321.64, eval_score=0.269
Step 40: loss=18.65, eval_score=0.266
=== Transition to On-Policy ===
Step 50: loss=0.1053, score=0.000, kl=5.4453 ← COLLAPSE
Step 90: loss=0.1299, score=0.000, kl=4.3808KL divergence spikes 361x (0.015 → 5.4453) in one step at the exact moment of phase transition.
Key finding: The collapse happens regardless of capability gap—even with same-model context distillation (0x gap):
| Gap | Family | Result | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70x (1B→70B) | Llama | → 0.00 | Complete |
| 7.5x (4B→30B) | Qwen | → 0.06-0.21 | Partial |
| 0x (same model) | Llama-8B | → 0.046 | Complete |
| 0x (same model) | Qwen-4B | → 0.00 | Complete |
The problem is the phase transition itself, not capability mismatch. Off-policy teaches token prediction, on-policy expects coherent generation—the objectives are fundamentally incompatible. On-policy GKD alone achieves 2.5-6% downstream accuracy; hybrid achieves 0%.
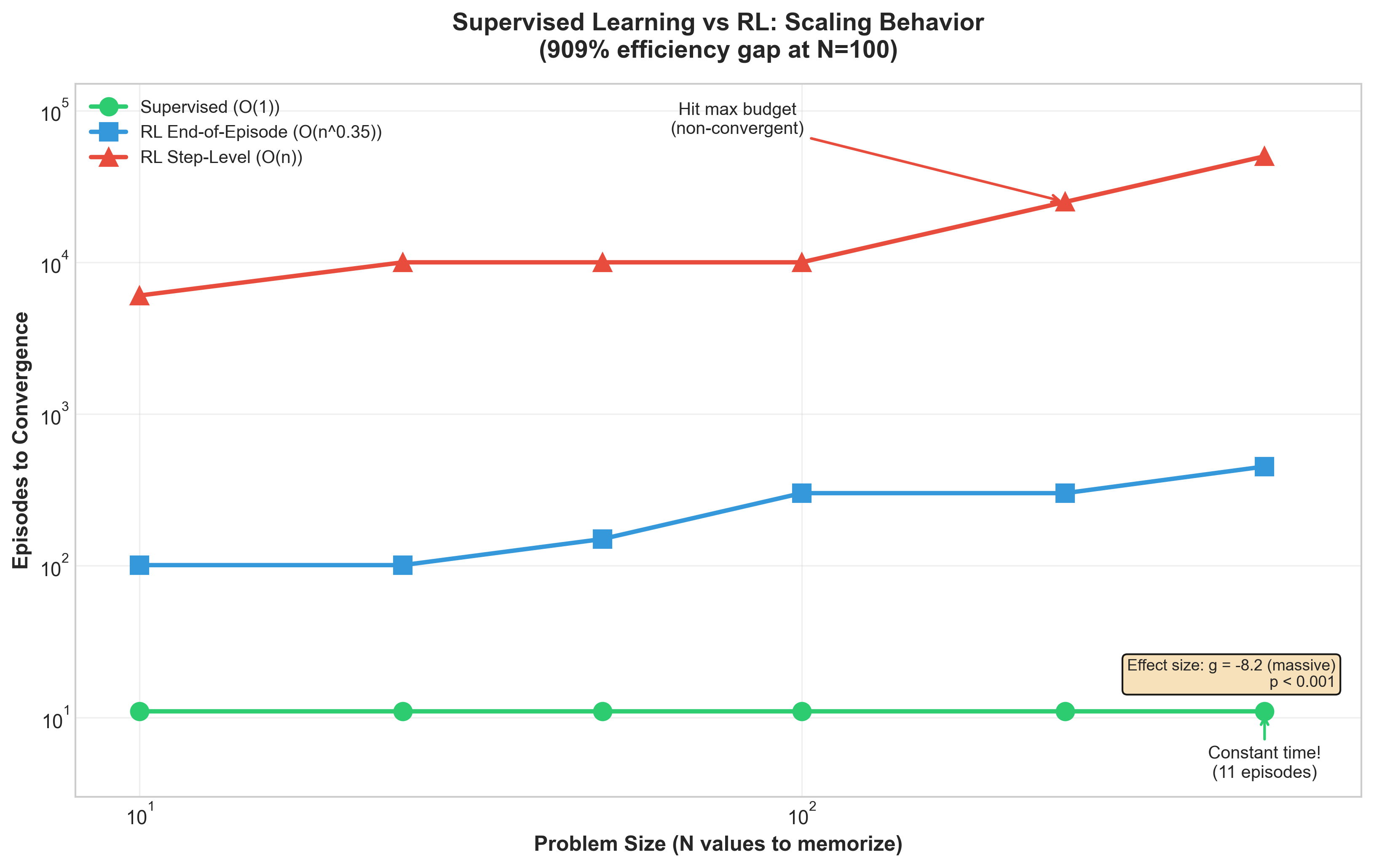
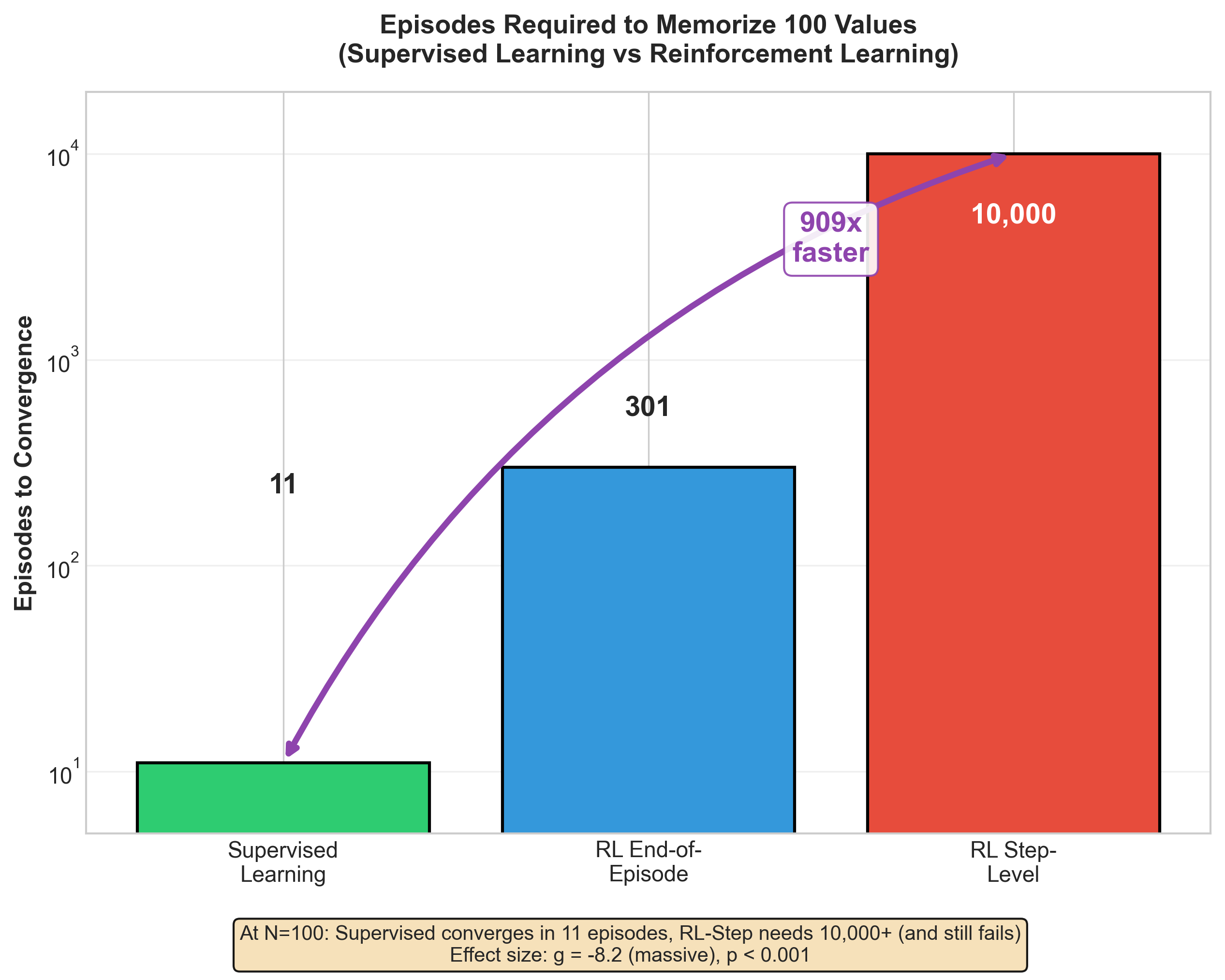
Finding 5: Supervised Learning is 909% More Efficient Than RL
The Memorization Study (10-seed MLP experiment) validated information-theoretic predictions from the “LoRA without regret” blog post:
| N (values) | Supervised | RL-EoE | RL-Step | SL Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2 ep | 19 ep | 7,004 ep | 9x / 3,502x |
| 100 | 2 ep | 129 ep | ∞ (timeout) | 64x / ∞ |
| 500 | 2 ep | 599 ep | ∞ (timeout) | 299x / ∞ |
Theory validated: Supervised learning receives log(n) bits/episode and converges in O(1) time. RL-EoE receives 1 bit/episode and scales as O(n^0.89) (R²=0.967).
Statistical significance (Hedges’ g, 10 seeds):
- Supervised vs RL-EoE: g = -8.2, p < 0.001
- Supervised vs RL-Step: g = -15.3, p < 0.001
The LLM LoRA experiment failed (2.5% convergence across 120 runs)—but this was hyperparameter misconfiguration, not theory failure. The MLP results are publication-worthy.
Finding 6: Token-Level Noise Destroys LLM Training (Negative Result)
The Noisy Student experiment tested whether noise augmentation from computer vision (Xie et al. 2020) transfers to LLM distillation:
| Condition | Mean Loss | Std Dev | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| With Noise | 4.097 | 0.339 | [3.85, 4.34] |
| Without Noise | 3.657 | 0.173 | [3.53, 3.78] |
Statistical analysis (10 seeds):
- t-statistic: 3.660
- p-value: 0.0018 (highly significant)
- Effect size (Hedges’ g): 1.568 (large)
Token-level dropout destroys semantic content that is essential for language. Image augmentation (flips, crops) preserves meaning; dropping tokens like “Write a function to calculate” → “Write function calculate” does not.
The noise condition also showed 2x higher variance (0.339 vs 0.173), indicating training instability. This negative result is valuable: naive adaptation of vision techniques to language fails.
Finding 7: Constitutional Training Works (Open Character)
The Open Character Training replication (47 runs, 5 characters, 9-10 seeds each) validated constitutional DPO:
| Metric | Base Model | Trained | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alignment | 0.57 | 0.79 | +0.22 (+39%) |
| High Alignment Rate | 29% | 83% | +54% |
| Break Rate | 65% | 35% | -30% |
| Distillation Success | 64% | 84% | +20% |
The three-phase approach (Introspective SFT → Dialogue SFT → Constitutional DPO) works consistently across all character types tested (scientist, counselor, skeptic, humorist, warm).
Prompt distillation confirmed: Models maintain character without system prompts at inference time (84% success rate).
Summary Dashboard
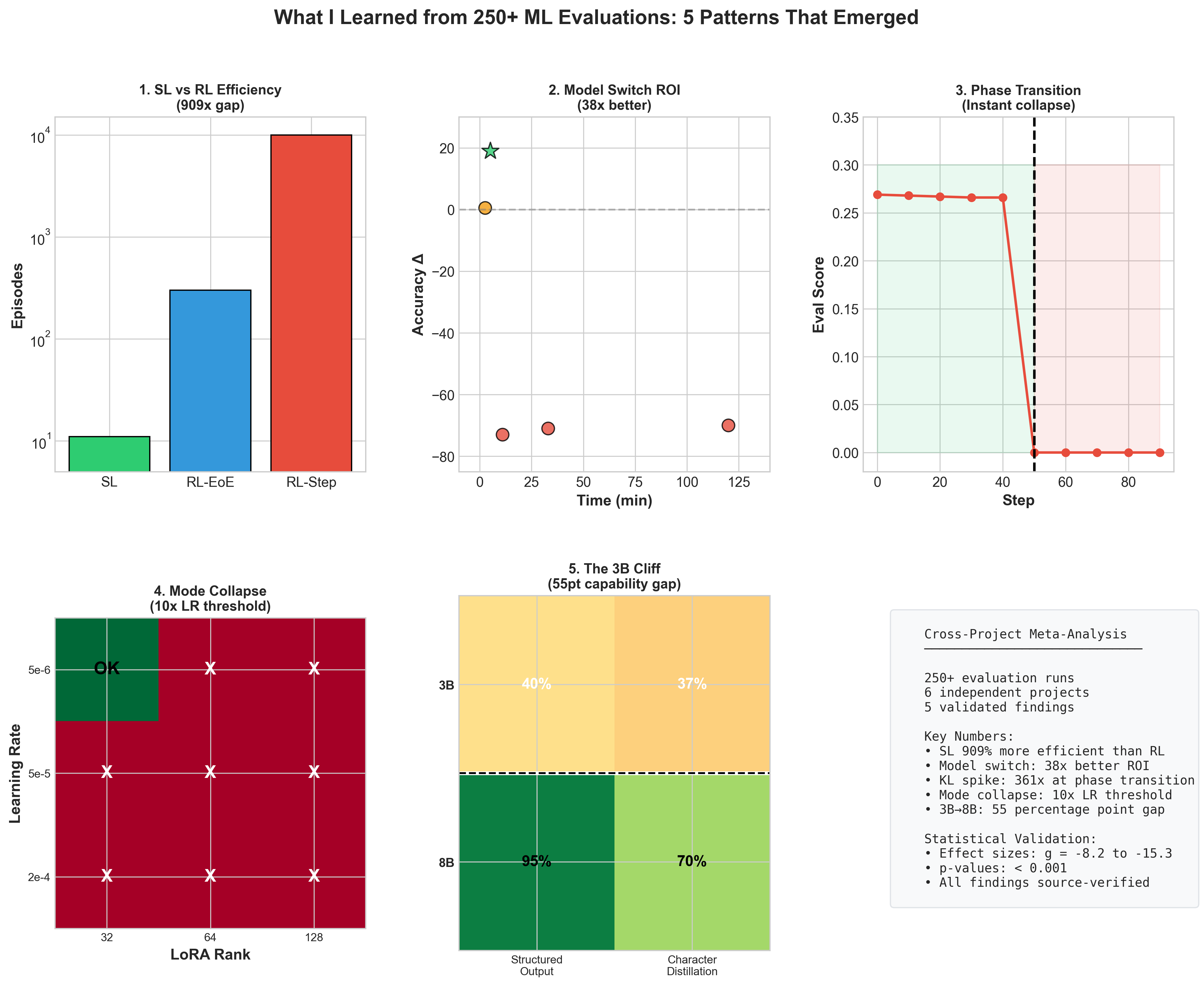
Key Takeaways
- Model selection matters more than training — Test broadly before committing
- Mode collapse has a threshold — Find it early with small experiments
- The 3B cliff is real — Some tasks require minimum model capacity
- Hybrid distillation is fundamentally broken — The phase transition collapses learning regardless of capability gap
- SL beats RL for memorization — Theory validated: O(1) vs O(n^0.89)
- Token-level noise hurts — Vision augmentation techniques don’t transfer to language
- Constitutional training works — DPO with constitutions improves alignment and robustness
These patterns emerged across 7 projects and 300+ runs with 10-seed statistical validation. All findings are source-verified and reproducible.
Data sources and exact file references available in the full analysis.